|
| Excel Table Example |
What is Excel Tables? What are the advantages of using the Excel Tables?
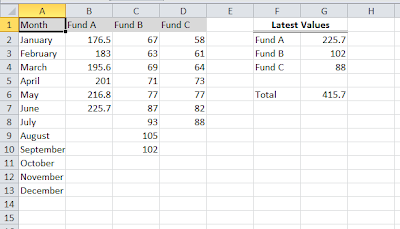
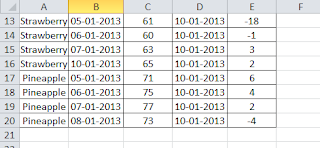
You might be thinking on these questions. For better understanding, let us look into a simple example. We have a data in the range A1 to E20 which talks about the different products, their price variations. By using Table, we are telling the excel that, The cells from A1 to E20 has related data and row 1 has table headers. Currently data is in only 19 rows. However it can be increased later. When you make a table in Excel, you can add rows without worrying about updating the formula references, formatting of cells, Filter settings etc.
Key Advantages of Excel Tables:
- Activating any cell in the table gives the access to a new Table Tools contextual tab on the ribbon
- Provides option to quickly apply background color and text color formatting by choosing from the gallery This formatting is optional.
- Each column header contains a drop down list which you can use to sort the data or filter the table to hide specific rows.
- If you scroll down the sheet so that the header row disappears, the table headers replace the column letters in the worksheet header. In simple words, you don’t need to freeze the top row of the table to keep the column labels visible
- Tables support calculated columns. A single formula in a column is automatically propagated to all cells in the column.
- Excel Tables supports structured references. Instead of using the cell references formula can use table names and column headers
- When you move your mouse pointer to the lower right corner of the lower right cell, you can click and drag to extend the table’s size, either horizontally(add more columns) or vertically(Add more rows).
- Selecting the rows and columns within the table is simplified
- When a workbook contains atleast one table, Excel doesn’t allow you to use the custom views features(choose view->Workbook Views-> Custom Views).
- You cannot insert automatic subtotals within a table(by choosing Data->Outline->Subtotal)