VLOOKUP in Excel is one of the most powerful and useful function which helps to save our time on many occasions. Some of the situations where VLOOKUP comes in handy are fetching data from other tables, matching two different series, creating one list from multiple related lists etc. This post is not on how to use VLOOKUP in excel. This post is all about some of the useful tricks which is helpful to use VLOOKUP in excel in an effective way.
VLOOKUP Tips and Tricks
-
Using the $ for lookup value and lookup range
When you are copy and pasting the VLOOKUP in excel to different cells, you might have noticed errors. This happens because while you are pasting the formula, range changes. To avoid this, you can use the absolute range or value. To make the value absolute you should use $ symbol.
For example, consider an example.
=vlookup(a2,c2:d5,2,false)
The above formula is there in cell G2. If you copy and paste the formula in G3, the formula changes to =vlookup(A3,C3:D6,2,false). If you copy the formula in the cell H2, then formula changes to =vlookup(B3,D2:E6,2,false). To avoid this, we can use $ or it is called absolute reference. $ makes the row or column absolute. If you use before column name then, the column will become absolute. If you use before row number, then row number will become absolute. Likewise, if you use $ before column and row number, then both column and row will become absolute. There are different ways to use absolute references in excel depending on the situations. Let’s learn more on this with the same example mentioned above.
Scenario 1: =VLOOKUP($A$2,$C$3:$D$6,2,false)- In this case, wherever you copy this formula, it will lookup for the value in cell A2 in range C3 to D5 of the active sheet.
Scenario 2: =VLOOKUP($A2,$C$3:$D$6,2,false)- Here lookup range and column of the lookup value remains constant. However, row number changes depending on where you paste the formula. This can be used when lookup value in there in column A.
Similarly, you can use the absolute reference for the range as well.
2. Understanding error values of VLOOKUP
Majorly, while using VLOOKUP in excel 3 errors values come out. They are #NAME, #N/A and #VALUE.
What is this means? How to fix it.
#NAME error in VLOOKUP: If you get #NAME error, then it means that there is a spelling error in the formula. Please check the syntax and fix it.
#VALUE error in VLOOKUP: This commonly appears when the column index number is less than the range you have selected. For example, if you have selected the column index number as 5 wherein the range has only 4 columns this error will come. Please check the lookup range and column index to fix this. Another possible cause might be lookup value length is more than 255 characters.
#N/A error in VLOOKUP: This is not necessarily an error. This means that the value you are looking for in the range is not available. The things you should check are
- Is lookup value is correct?
- Are any blank spaces before or after the lookup value? If yes use trim or clean functions to remove spaces.
- Have you had selected the range where the first column has the value you are looking for lookup value? -If no, select the range such way that, a column on which you are looking for the lookup value should be the first column in the range. The format of the lookup value and lookup range should be same.
3. Working with errors
When the lookup value is not available in lookup range, VLOOKUP gives error #N/A. If you are using the further calculation based on the resulting result, then that also shows as #N/A. To hide this or to make cells look cleaner you can use the formula IFERROR with VLOOKUP. It will look like this IFERROR(VLOOKUP(….), “VALUE to be WRITTEN IN CASE OF ERROR”)).
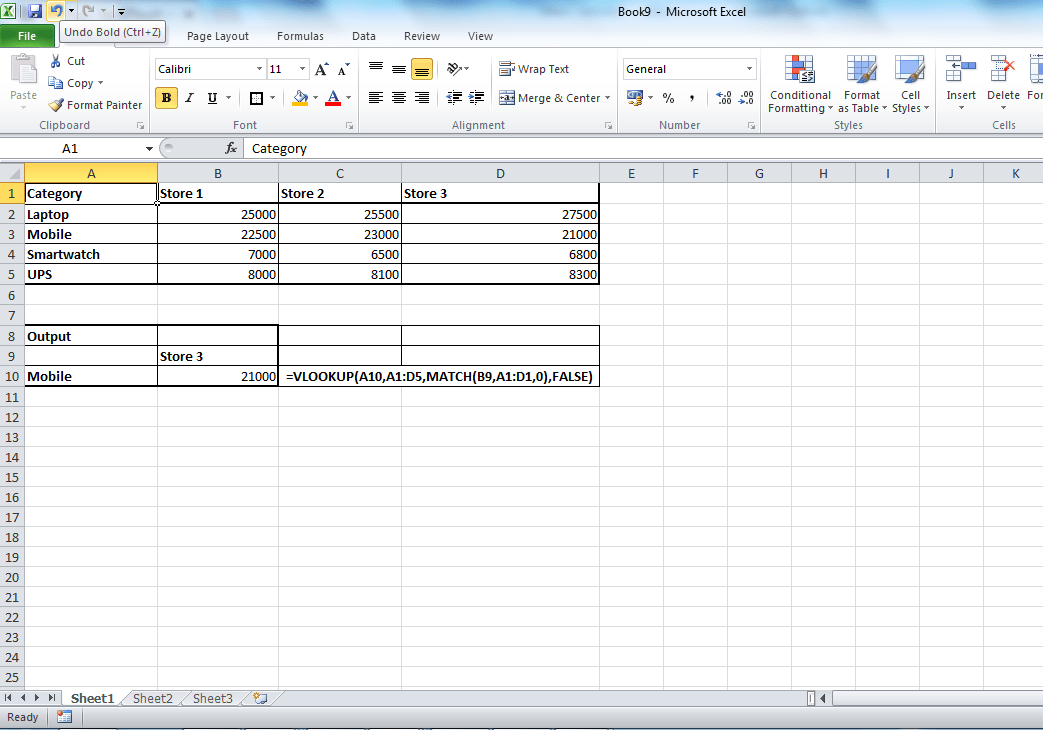
4. ROW and COLUMN VLOOKUP or multi conditional VLOOKUP
We already know that VLOOKUP in EXCEL can be used for fetching data based on the lookup value. But how to use multi conditional VLOOKUP in EXCEL. This means that the resulting data should be matched with both row and column. This can be done with help of MATCH function with VLOOKUP. You need to replace, column index or 3rd argument of VLOOKUP with match function.
Example for the same is as mentioned below.
=VLOOKUP($A9,$A$1:$D$6,MATCH(B$8,$B$1:$D$1,1)+1,FALSE)
You can read more on this here.
5. Partial match with VLOOKUP
Making forth argument of VLOOKUP as TRUE will perform partial match. But it has many restrictions. Instead, you can use wildcard characters in VLOOKUP function to perform partial match. Basic wildcard charecter for partial match are,
“*”: Find any number of characters after or before text. For example, you can use “Te*” to match the text “Text” from a list or *Te to match the text “Forte”.
“?”: Use a question mark to replace with a character. For example, you can use “?aste” to lookup for the text “Waste” or “Taste”.
These are the basic yet effective VLOOKUP tips to make your work easier and use this function more effeciently. If you have any queries do write in the comment section below.