VLOOKUP in Excel is a powerful function. Simple vlookup does search for the value in the left most column in the table and returns the value in the same row from column number provided. If the requirement is to search for both row and column, then we need to use a conditional VLOOKUP in Excel. This needs clubbing of match function with vlookup.
Recommended Reading:
VLOOKUP in EXCEL tips and Tricks
Find matching value in a row and return column name in Excel
Conditional VLOOKUP in Excel with Match Function
There are many ways to do conditional VLOOKUP in EXCEL. In this post we will learn one of the simple method to achieve this. For that, we need to use MATCH Excel function.
By default, we need to enter the column number in the VLOOKUP syntax. To do conditional vlookup which does checks for both row and column, replace column number with match function. The syntax will look like below.
VLOOKUP( lookup_value, table_array, MATCH (lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type]), [range_lookup] )
Explanation on how it works
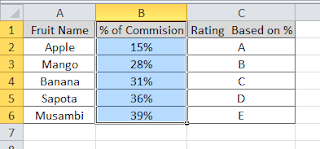
Lets a take a simple example. Refer the table below. The row has store details and in column has categories. To return corresponding value by matching both row and column, this conditional vlookup formula will help.
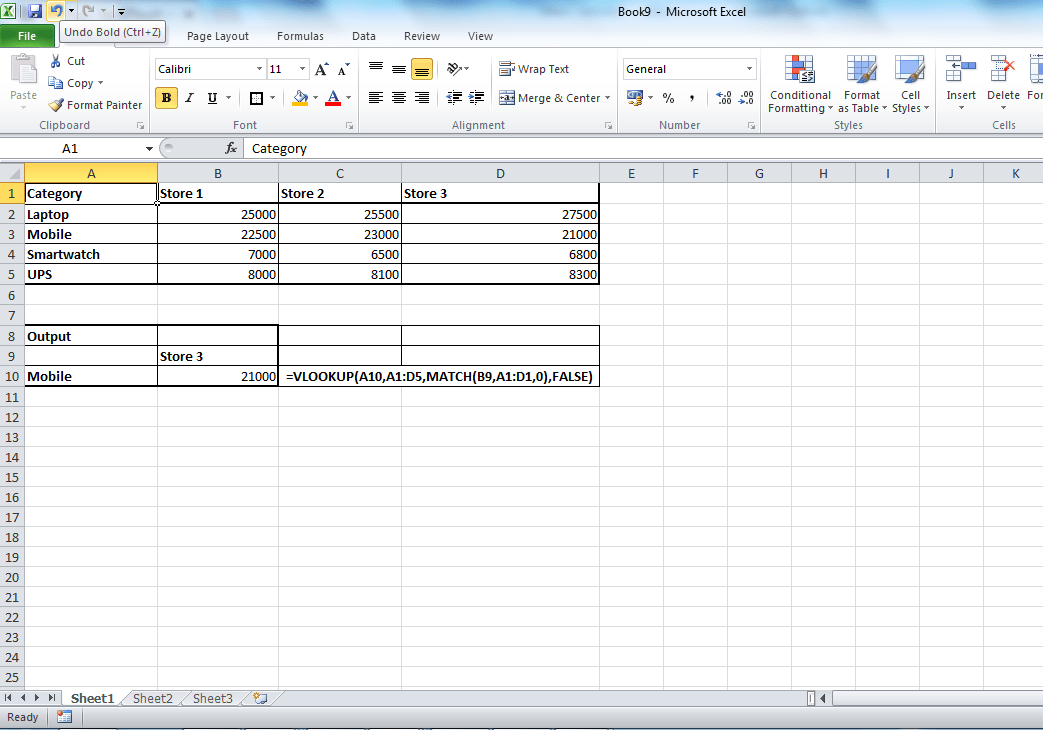
Formula used here is
=VLOOKUP(A10,A1:D5,MATCH(B9,A1:D1,0),FALSE)
In this example, instead of hard coding the column number, we have used match function. MATCH function return the relative position of an item in an array that matches a specified value in a specified order. In our example it return the column number of the row header Store 3.
Syntax for Excel MATCH function is
=MATCH(lookup value, lookup array, [match type])
This can be achieved through combination of match and index formula too. However, personally for me this is the most convenient way to do row and column vlookup in excel. If you have any specific queries on VLOOKUP in excel, feel free to write to us in the comment section below.